Science of the Total Environment揭示天然有机质-矿物交互作用对阴离子及阳离子化学形态的影响机制.docx
作者: 来源:农田有机污染生物消减创新团队 2022-10-21
Science of the Total Environment:揭示天然有机质-矿物交互作用对阴离子及阳离子化学形态的影响机制

话题:天然有机质,金属氧化物,吸附,表面络合模型
天然有机质(NOM)和金属氧化物是重要的土壤组分,参与诸多环境化学过程。一些研究表明,NOM可强烈吸附在金属氧化物表面,影响环境中养分及污染物的迁移及生物有效性。表面络合模型是研究离子化学形态的有力工具,其中多表面模型(MSM)将离子在不同吸附界面的吸附进行加和,不考虑NOM-金属氧化物交互作用对离子吸附和吸附界面性质的影响,可成功预测金属阳离子的化学形态,但不能准确预测阴离子在土壤中的吸附。目前,对于阴离子和阳离子出现此差异结果的机制还不清楚。天然有机质-电荷分配(NOM-CD)模型考虑了NOM对阴离子吸附的竞争作用,可成功预测阴离子在土壤中的化学形态。然而,如何在同一模型框架下同时预测阴离子和阳离子的化学形态仍是一大挑战。为了更好地理解NOM-矿物交互作用对离子吸附的影响,需要对NOM在矿物表面的空间分布进行研究。
本文系统研究了NOM和金属氧化物交互作用对重金属阳离子和阴离子吸附的的影响,通过吸附实验和表面络合模型计算等手段,阐明了天然有机质在金属氧化物表面纳米尺度内的空间分布特征,揭示了其对于阴离子及阳离子化学形态分布的微观机制。
相关成果发表于SCI期刊Science of the Total Environment(IF= 10.753)。
农业农村部环境保护科研监测所博士生李金波为该论文第一作者,翁莉萍研究员为通讯作者。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金和国家重点研发计划项目的资助。
DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153259
Abstract:
In this study, the nano-scale spatial distribution of natural organic matter (NOM) on the surface of iron (hydr)oxides and its relevance to oxyanion (PO43−) and metal cation (Cd2+ and Cu2+) adsorption to the assemblage of oxide (goethite) and NOM (humic acids (HA) or fulvic acids (FA)) was investigated with experiments and advanced surface complexation modeling. Both the linear additive Multi-Surface model (MSM) and the more sophisticated Natural Organic Matter-Charge Distribution (NOM-CD) model were used. The MSM model ignores the effects of NOMmineral interaction on ion adsorption, whereas the NOM-CD model considers this effect. The results showed that with the increase of NOM loading on oxides, deviation between the MSM and NOM-CD model became bigger for PO43−, but smaller for Cd2+ and Cu2+. Oxyanions bind mainly to oxides and therefore the competitive effect of NOM cannot be neglected, which explains the large difference between these two models for PO43−. On the contrary, at a relatively high NOM loading, a large fraction of NOM extends further away from the surface of oxides. Thus for metal cations that bind mainly to NOM, the influence of NOM-mineral interaction on their adsorption is small and the results of the MSM and NOM-CD model are similar. In top soils, the NOM loading on oxides is often high, therefore the linear additive MSM is applicable for metal cation speciation calculations as reported in many literatures. An approach based on the NOM-CD model was proposed, which can not only calculate the macroscopic solid-solution distribution of both cations and anions, but can also provide information regarding their microscopic surface speciation.
Keywords:
Natural organic matter;Mineral;Heavy metals;Adsorption;Surface complexation model
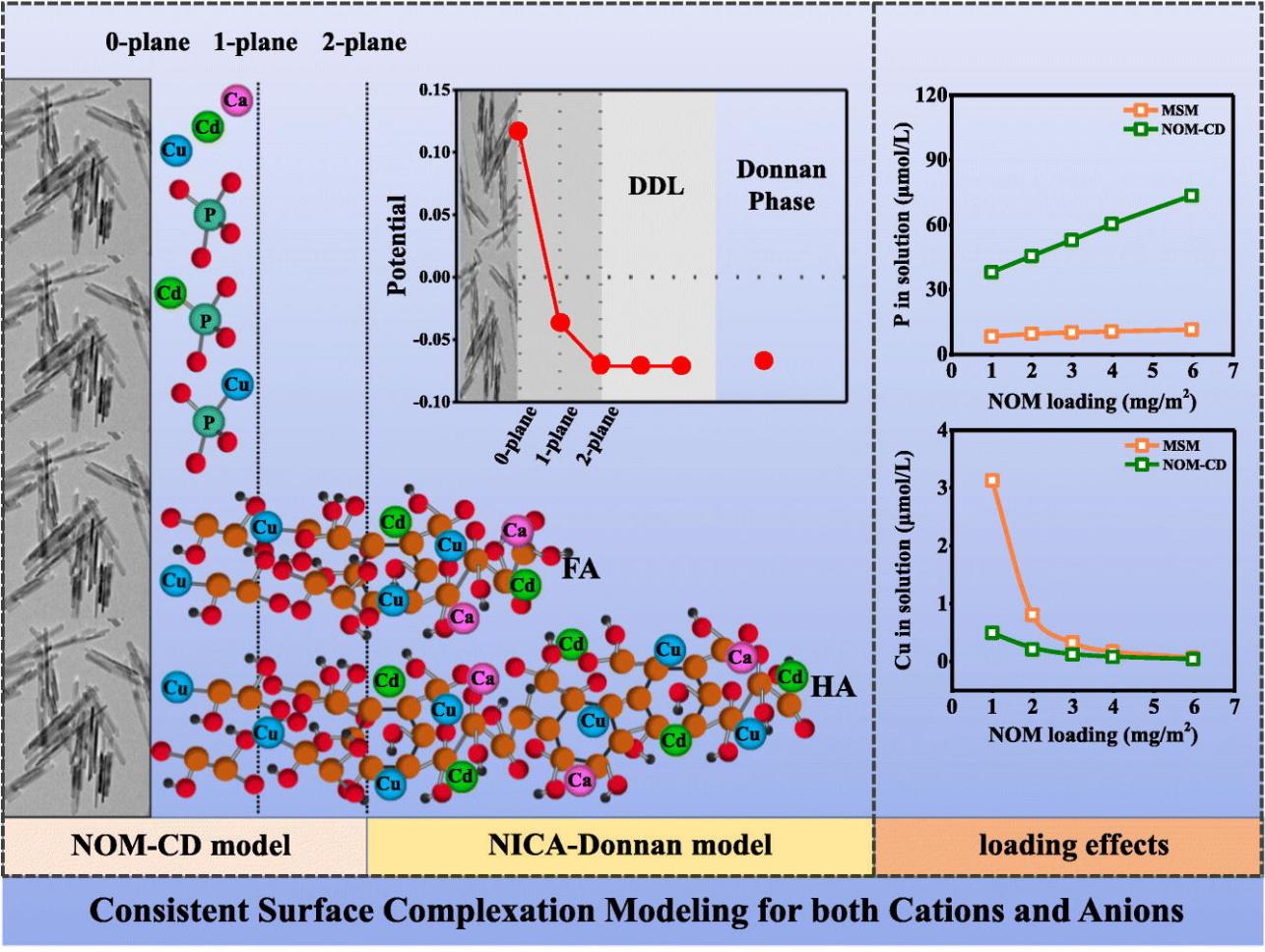
主要研究结果:随着有机质在金属氧化物表面负载量的增加,MSM模型和NOM-CD模型对PO43-吸附的预测结果差距逐渐增大,对Cd2+和Cu2+吸附的预测结果差距逐渐减小。阴离子主要吸附在氧化物上,NOM的竞争作用不可忽视。而金属阳离子主要吸附在有机质上,在有机质负载量较大时,大部分的有机质在矿物表面Stern层之外,这部分有机质不受矿物表面的影响,因此NOM和矿物的交互作用对金属阳离子的吸附影响较小。基于NOM-CD模型发展的统一模型框架,不仅可同时计算阴离子及阳离子宏观的固液分配,还可以揭示微观的表面化学形态信息。
环境意义:天然有机质和矿物的交互作用影响许多环境过程,是科学研究的热点问题。探究有机质在矿物表面纳米尺度内的空间分布特征是一大挑战,表面络合模型是研究NOM-矿物交互作用对离子吸附影响的有力工具,同时可以离子为探针揭示有机质在矿物表面的纳米尺度内的空间分布特征。本研究阐明了阳离子及阴离子在土壤中的主要吸附界面分别为天然有机质及金属氧化物,有机质对于阴离子吸附的竞争作用不可忽视。基于NOM-CD模型发展的统一模型框架可应用于环境中阳离子型及阴离子型污染物的风险评估。













