Science of the Total Environment:土施硫酸锰能够显著土壤镉有效态和镉在小麦植株体内的转运和积累
作者: 来源:重金属团队 2022-10-26
Science of the Total Environment:土施硫酸锰能够显著土壤镉有效态和镉在小麦植株体内的转运和积累
农业农村部环境保护科研监测所重金属团队在 Science of the Total Environment杂志发表题为"Soil application of manganese sulfate effectively reduces Cd bioavailability in Cd-contaminated soil and Cd translocation and accumulation in wheat "的最新研究成果。
农业农村部环境保护科研监测所助理研究员黄青青和河南工业大学环境工程学院王雅乐老师为共同第一作者,农业农村部环境保护科研监测所徐应明研究员为通讯作者。研究得到中国农业科学院创新工程项目,现代农业产业技术体系项目以及耕地重金属污染防治联合攻关计划项目的资助。
Abstract:
Cadmium (Cd) pollution in wheat fields has caused serious food safety issues in China. Manganese (Mn)-containing materials have been widely used in paddy fields to reduce Cd accumulation in rice. However, the remediation effects of MnSO4 in wheat fields have not been well studied and the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. Our field experiment showed that the application of 0.1% and 0.2% MnSO4 in soil reduced Cd concentrations significantly in wheat root, stem, leaf, and grain by 26.67–30.76%, 15.78–29.30%, 22.03–30.66%, and 30.57–50.55%, respectively, while increasing Mn concentrations significantly in these wheat tissues. MnSO4 application significantly increased soil available Mn content by 3.78–6.19 times, the free Mn oxides and amorphous Mn oxides by 1.72–10.38 times, and Mn oxides bound Cd contents by 10.23–39.55%, resulting in a reduction of Cd availability by 30.11–40.78%. Simultaneously, MnSO4 treatment altered the chemical forms of Cd and Mn, promoted the soluble protein concentration, and decreased the malondialdehyde (MDA) content in wheat roots. Additionally, soil application of MnSO4 down-regulated the expression of TaNramp5, TaHMA2, and TaLCT1 in wheat roots, mediating the reduction of wheat root Cd concentration, and increased the sequestration of Cd into vacuoles by up-regulating the expression of TaHMA3. These findings add to the current knowledge of how MnSO4 affects Cd mobilization and absorption via different mechanisms occurring both in the soil medium and at the plant level. This research indicates that soil application of MnSO4 has great potential to remediate Cd-contaminated wheat fields.
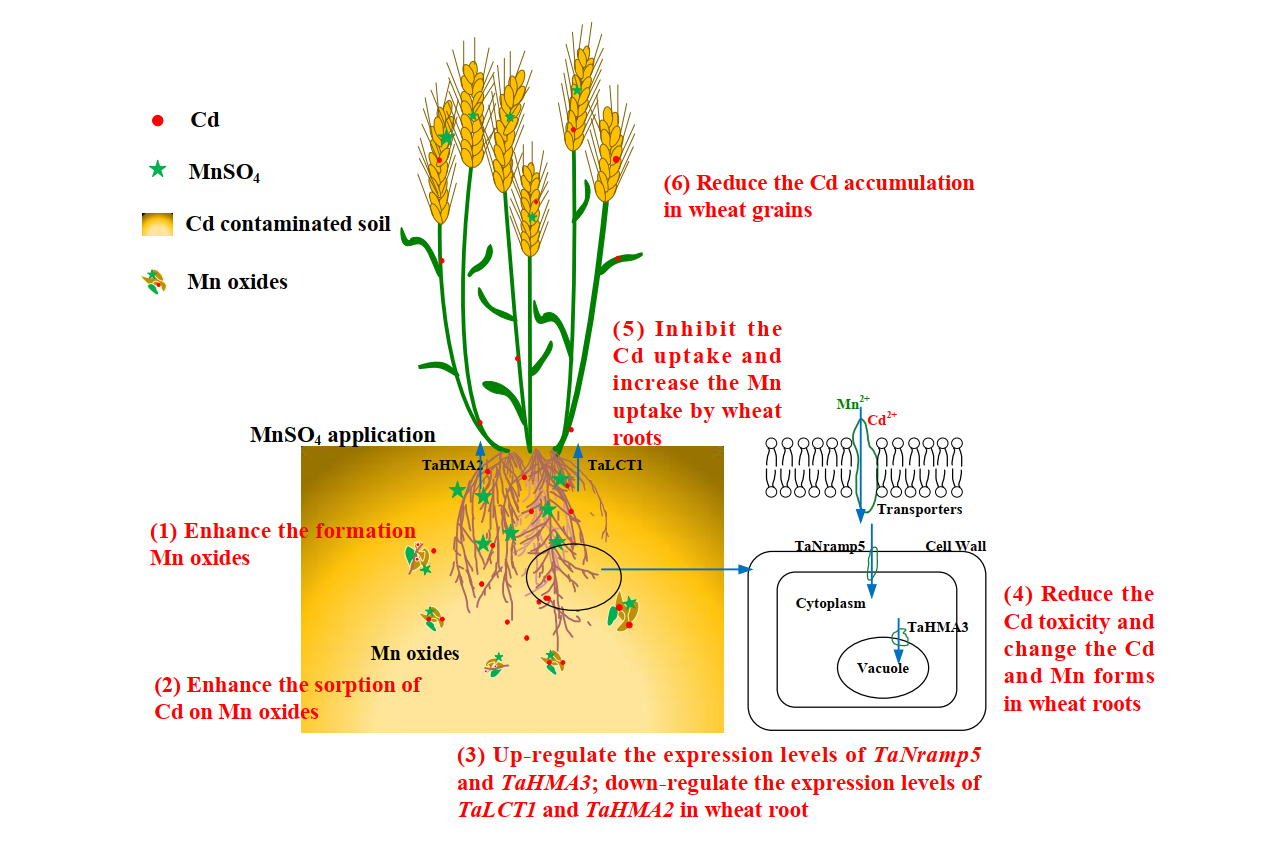
小麦是我国重要的粮食作物,近年来我国北方小麦镉污染风险逐渐显露,严重影响了农业安全生产。因此,降低小麦镉含量,提高小麦品质和保障食品安全是目前农业生产上急需解决的问题之一。锰是植物生长的有益元素,有助于增强植物对逆境胁迫的抵御能力,尤其是在缓解重金属对植物毒害中发挥着重要作用。但是目前关于小麦体内的锰镉拮抗作用及锰肥对小麦镉吸收的影响研究相对较少。
本文通过大田小区试验和盆栽试验研究了土施锰肥(硫酸锰)对弱碱性镉污染小麦土钝化效应以及对小麦籽粒镉累积的降镉效果与机制。土施硫酸锰能够提高土壤锰氧化化物对镉离子的吸附,从而改变土壤中镉的赋存形态,促进镉由可交换态向稳定态转换,降低土壤镉的生物有效性,最终降低小麦根系对镉的吸收以及小麦籽粒镉的累积。同时,在植物体内土施硫酸锰能够提高小麦的抗氧化系统,改变根系中镉的化学形态分布和亚细胞分布,以及影响小麦根部与镉吸收和转运相关基因的表达。这些发现可为我国北方弱碱性镉污染小麦田上小麦安全生产提供理论依据和技术支持。













