Biochar揭示生物炭纳米颗粒与铁矿物纳米颗粒的稳定性与相互作用:pH、离子强度和溶解性有机质的影响.docx
作者: 来源:有机污染生物消减团队 2022-10-21
Biochar:揭示生物炭纳米颗粒与铁矿物纳米颗粒的稳定性与相互作用:pH、离子强度和溶解性有机质的影响

话题:生物炭,铁矿物,纳米颗粒,量子化学计算
农业农村部环境保护科研监测所有机污染生物消减团队在Biochar杂志发表题为"Stability and interaction of biochar and iron mineral nanoparticles: effect of pH, ionic strength, and dissolved organic matter" 的研究论文,采用沉降实验。DLOV理论和量子化学计算等手段,探讨了生物炭纳米颗粒与铁矿物纳米颗粒的稳定性与相互作用和相关影响机制。相关成果发表于SCI期刊Biochar(IF= 11.452)。
农业农村部环境保护科研监测所硕士研究生刘勇为论文第一作者,马杰副研究员和翁莉萍研究员为论文共同通讯作者。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金和农业农村部环境保护科研监测所所及重点项目的资助。
DOI:10.1007/s42773-022-00172-z
Abstract:
Biochar nanoparticles (BCNPs) and iron mineral nanoparticles (IMNPs), such as ferrihydrite nanoparticles (FHNPs), magnetite nanoparticles (MTNPs), and goethite nanoparticles (GTNPs), are often combined and used in soil remediation. However, the stability and interaction of nanoparticles under various environmental conditions have not been investigated previously. In this study, settling experiments, a semi-empirical model, the Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek (DLVO) theory, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observations, and quantum chemical calculations were used to study the interaction and heteroaggregation of BCNPs and IMNPs. Settling of BCNPs-FHNPs and BCNPs-GTNPs was stable at neutral and alkaline pH (relative concentration of unsettled nanoparticles Cres’ = 0.679–0.824), whereas fast settling of BCNPs-IMNPs was observed at acidic pH (Cres’ = 0.104–0.628). By contrast, BCNPs-MTNPs consistently showed moderate settling regardless of the mass of magnetite at all pH (Cres’ = 0.423–0.673). Both humic acid (HA, 10 mg L−1) and ionic strength (IS, 10 and 100 mM) facilitated the settling of BCNPs-FHNPs and BCNPs-MTNPs systems, whereas the settling of BCNPs-GTNPs was sensitive only to IS. Fulvic acid (10 mg L−1) had a general stabilizing effect on the BCNPs-IMNPs systems. The results of SEM and quantum chemical calculations suggested that the interaction between BCNPs and FHNPs (-2755.58 kJ mol−1) was stronger than that between BCNPs and GTNPs (−1706.23 kJ mol−1) or MTNPs (−1676.73 kJ mol−1). The enhancement of heteroaggregation between BCNPs and IMNPs under unfavorable conditions (acidic pH, HA, and IS) was regulated by the strength of the interaction. Therefore, the enhancement of heteroaggregation of BCNPs-FHNPs was greater than that of BCNPs-MTNPs. In the BCNPs-GTNPs system, the high concentration and elongated structure of GTNPs may contribute greatly to heteroaggregation and settling with small interactions. Our results highlight the influence of pH, IS, and HA on the interaction between BCNPs and IMNPs. These results will be helpful in the application of BCNPs and IMNPs for soil remediation.
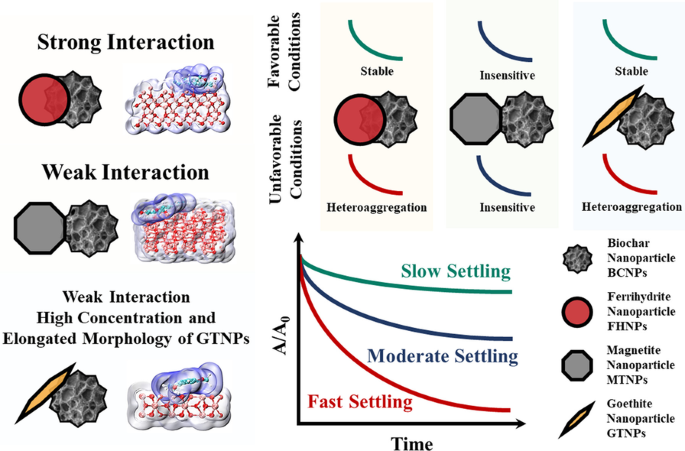
铁矿物纳米颗粒(IMNPs)(水铁矿纳米颗粒(FHNPs)、磁铁矿纳米颗粒(MTNPs)和针铁矿纳米颗粒(GTNPs))和生物炭纳米颗粒(BCNPs)在自然界中尤其是土壤当中广泛存在。目前,尽管有大量的研究人员对单独存在的IMNPs和BCNPs的环境行为进行了探讨,但尚未系统研究IMNPs和BCNPs共存时的相互作用。本研究通过沉降试验和动力学模型研究了IMNPs和BCNPs共存的稳定性以及环境因素的影响,并通过扫描电子显微镜和量子化学计算等手段揭示了纳米颗粒间的相互作用机制。BCNPs-FHNPs和BCNPs-GTNPs的沉降在中性和碱性pH下稳定(未沉降纳米颗粒的相对浓度Cres'=0.679–0.824),而在酸性pH下,BCNPs-FHNPs和BCNPs-GTNPs一般较容易沉降(Cres'=0.104–0.628)。相比之下,在所有pH值下,BCNPs-MTNPs始终表现出中等沉降的特征(Cres'=0.423–0.673)。腐殖酸(HA,10mg L−1)和离子强度(IS,10和100 mM)可促进BCNPs-FHNPs和BCNPs-MTNPs的沉降,而BCNPs-GTNPs的沉降仅对IS敏感。总体上看,富里酸(10 mg L−1)对BCNPs-IMNPs具有稳定作用。通过量子化学计算可知,BCNPs和FHNPs之间的相互作用(-2755.58 kJ mol−1)比BCNPs和GTNPs(−1706.23kJ mol−1)或MTNP(−1676.73kJ mol−1)更强。BCNPs和IMNPs结合关系的SEM图像也可以佐证上述相互作用大小关系。这种相互作用在一定程度上控制BCNPs和IMNPs之间异质聚集,并且在不利于纳米颗粒稳定的条件下(酸性pH、HA和IS)更为明显。因此,BCNPs-FHNPs异质聚集的增强作用大于BCNPs-MTNPs。而在BCNPs-GTNPs系统中,虽然BCNPs-GTNPs相互作用能大小居中,GTNPs的高浓度和棒状结构促进异质聚集和沉降。我们的结果阐明了pH、IS、HA,以及BCNP和IMNP之间相互作用对其沉降的影响机制,有助于BCNPs和IMNPs在土壤修复中的应用。













