Journal of Hazardous Materials:两步法改性海泡石及其对镉污染水和土壤的修复性能
作者: 来源: 2022-10-26
Journal of Hazardous Materials:两步法改性海泡石及其对镉污染水和土壤的修复性能
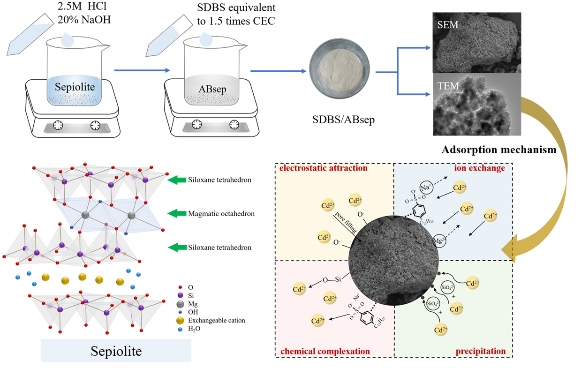
Abstract To enhance the remediation capability of cadmium (Cd) polluted water and soil, our approach involved two-step modification of sepiolite (Sep) through acid-base compound treatment and sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (referring as SDBS/ABsep), and then the batch adsorption and soil culture experiments were conducted to investigate its immobilization potential and mechanisms of Cd. The findings revealed that the SDBS/ABsep had a rougher surface and higher porosity, and the maximum adsorption capacity of Cd2+ onto SDBS/ABsep was 241.39 mg·g–1, which was 5.32 times higher than that on Sep. It conformed to the pseudo-second-order kinetic and Redlich-Paterson isotherm models. SDBS/ABsep exhibited a high efficiency for immobilization-induced remediation of Cd polluted soils. Upon the addition of different concentrations of SDBS/ABsep, DTPA–Cd content decreased by 17.41–47.33% compared with the control groups, and the ratio of residual fraction–Cd increased from 4.67% in unamended soil to 14.05% in the presence of 4% SDBS/ABsep. SEM-EDS, TEM, FTIR, XRD, and XPS analyses indicated that the interaction mechanisms between SDBS/ABsep and Cd included the electrostatic force, precipitation, ion exchange, and complexation of sulfonic acid groups. Therefore, SDBS/ABsep can be used as a promising effective passivation agent for remediation of Cd contaminated soil and water.
随着经济的发展和工业化进程的加快,土壤重金属污染已成为一个严重的问题,大量的镉(Cd)进入了农业土壤。我国土壤污染现状的调查显示,镉污染在土壤样品中的超标率排名第一(7.0%),超过了中华人民共和国环保部规定的限值。化学钝化修复是指利用固定剂或改良剂来改变重金属的化学形态,从而达到降低重金属在土壤中的生物利用度的目的,而粘土矿物因其成本低、性能好、破坏程度低等优点,被广泛应用于镉污染土壤的修复中。天然海泡石具有独特的纤维结构和内部通道,通过化学络合、离子交换、沉淀等修复机制,能有效降低重金属的迁移率和生物可利用度,但同时也存在一些局限性,如堵塞腔体、金属结合常数相对较小、选择性低、应用剂量大等。
为提高海泡石(Sep)对镉污染水体和土壤的修复能力,本研究采用酸碱复合处理和十二烷基苯磺酸钠(SDBS/ABsep)两步改性制备功能化海泡石,然后进行静态吸附和土壤培养实验,研究其对镉的固定潜力和机制。结果表明,SDBS/ABsep对Cd2+的最大吸附量为241.39 mg·g–1,约为Sep的5.32倍,符合准二级动力学模型和Redlich-Paterson等温线模型。SDBS/ABsep对Cd污染土壤的固定化修复效果良好。添加不同浓度的SDBS/ABsep后,土壤DTPA-Cd含量较对照组降低17.41 ~ 47.33%,残余Cd含量由未处理土壤的4.67%增加到14.05%。SEM-EDS、TEM、FTIR、XRD和XPS分析表明SDBS/ABsep与Cd的相互作用机制包括静电作用、沉淀、离子交换和磺酸基团络合作用。研究表明,SDBS/ABsep对Cd污染的水和土壤具有良好的修复潜力。
本研究得到国家重点研发计划项目和国家自然科学基金的支持。













